Dr. Goellner's Research Projects
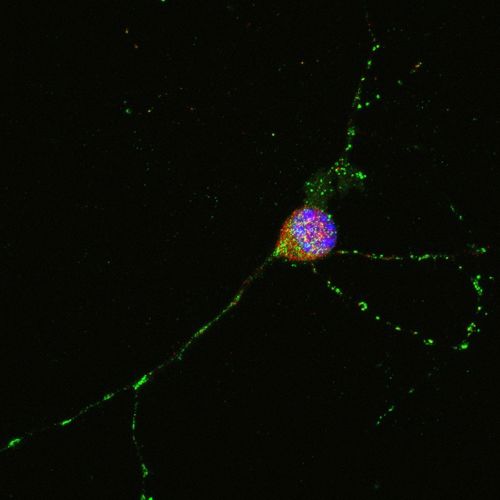
My laboratory is actively investigating neuronal proteins that contain polyglutamine (polyQ) stretches within their primary amino acid sequence. PolyQ proteins are fascinating, as a number of severe neurodegenerative disorders, such as Huntington’s Disease, are caused by mutation of the polyQ stretch within their respective proteins. Interestingly, the longer the polyQ expansion mutation- the more severe disease manifests.
We have identified, and are functionally characterizing, the novel polyQ containing protein- FAM171B- which has approximately 14 contiguous glutamines within its primary amino acid sequence. Specifically, we are asking questions such as: is FAM171B expressed in the nervous system? Might expansion mutation in FAM171B’s polyQ stretch cause neurodegenerative disease? Where does FAM171B localize within the cell? With which other proteins does FAM171B interact? In short, what “normal” function does FAM171B perform for the cell?
Using standard molecular/cell biological techniques (Ex. PCR, gel electrophoresis, cloning, immunoprecipitation, in situ hybridization, immunohistochemistry, and confocal fluorescence microscopy) my students and I are actively investigating the novel protein FAM171B, and contributing to the fascinating field of polyQ protein biology.

